Correction for Duin et al., Mode of action uncovered for the specific reduction of methane emissions from ruminants by the small molecule 3-nitrooxypropanol | PNAS

Mode of action uncovered for the specific reduction of methane emissions from ruminants by the 3-nitrooxypropanol | Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology
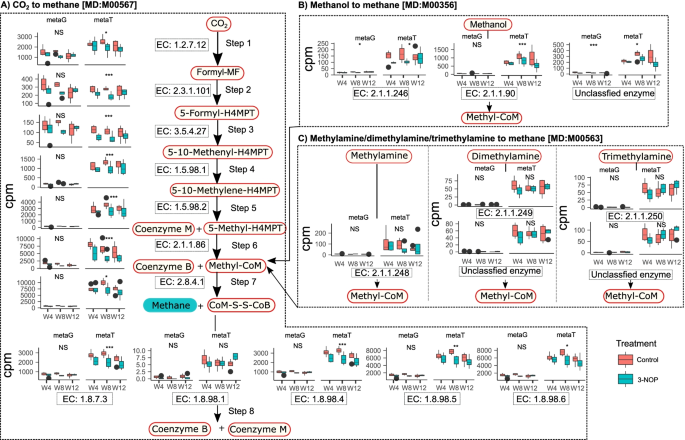
The effect of 3-nitrooxypropanol, a potent methane inhibitor, on ruminal microbial gene expression profiles in dairy cows | Microbiome | Full Text

Mode of action uncovered for the specific reduction of methane emissions from ruminants by the 3-nitrooxypropanol | Max-Planck-Institut für terrestrische Mikrobiologie
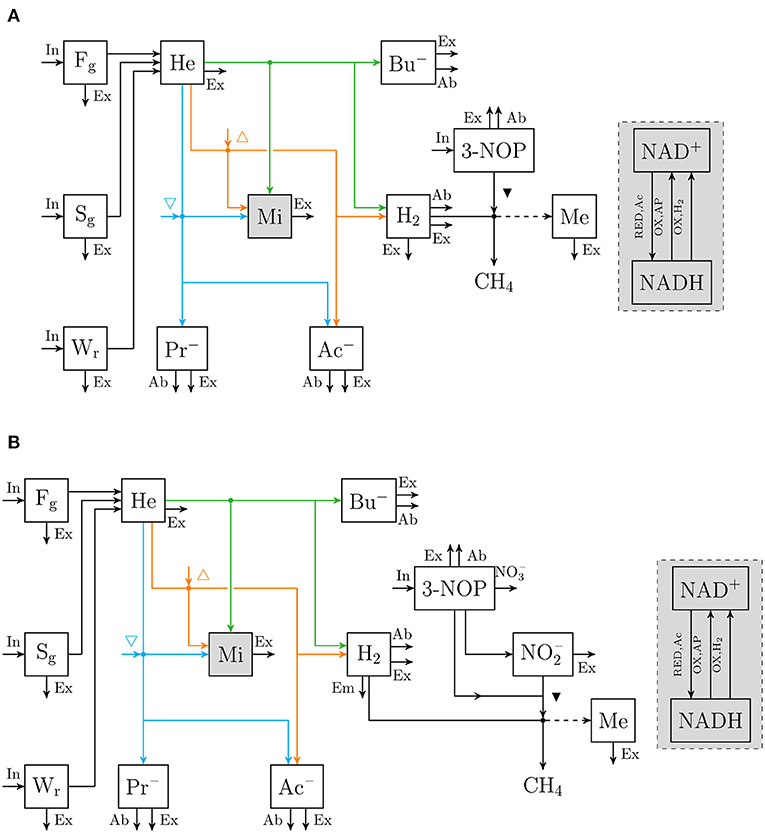
Frontiers | Inhibited Methanogenesis in the Rumen of Cattle: Microbial Metabolism in Response to Supplemental 3-Nitrooxypropanol and Nitrate

Binding of 3-NOP to methyl-coenzyme M reductase (MCR) as suggested by... | Download Scientific Diagram

Full article: Use of 3-nitrooxypropanol as feed additive for mitigating enteric methane emissions from ruminants: a meta-analysis

Mode of action uncovered for the specific reduction of methane emissions from ruminants by the small molecule 3-nitrooxypropanol | PNAS
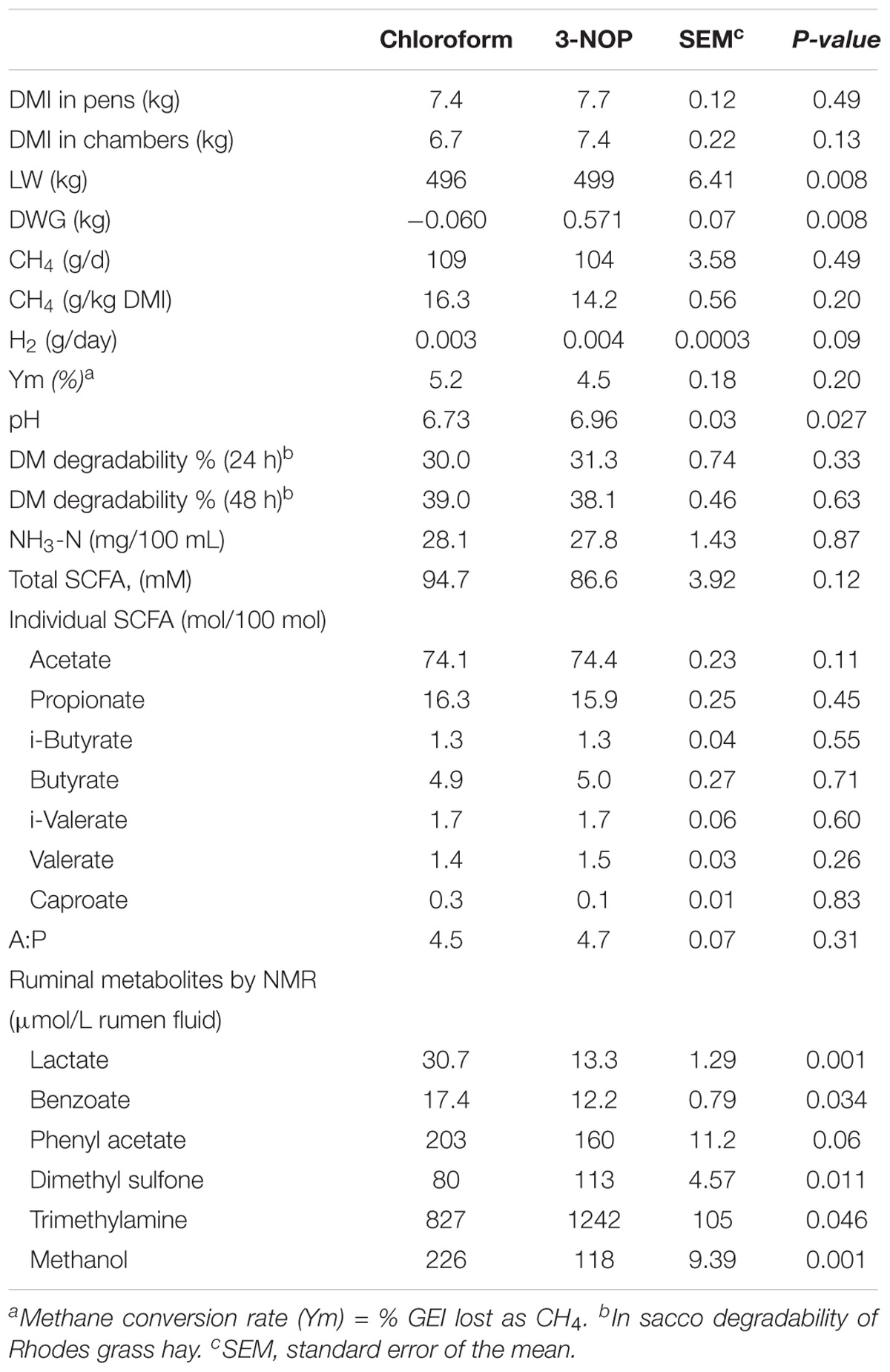
Frontiers | 3-NOP vs. Halogenated Compound: Methane Production, Ruminal Fermentation and Microbial Community Response in Forage Fed Cattle

Mode of action uncovered for the specific reduction of methane emissions from ruminants by the small molecule 3-nitrooxypropanol | PNAS
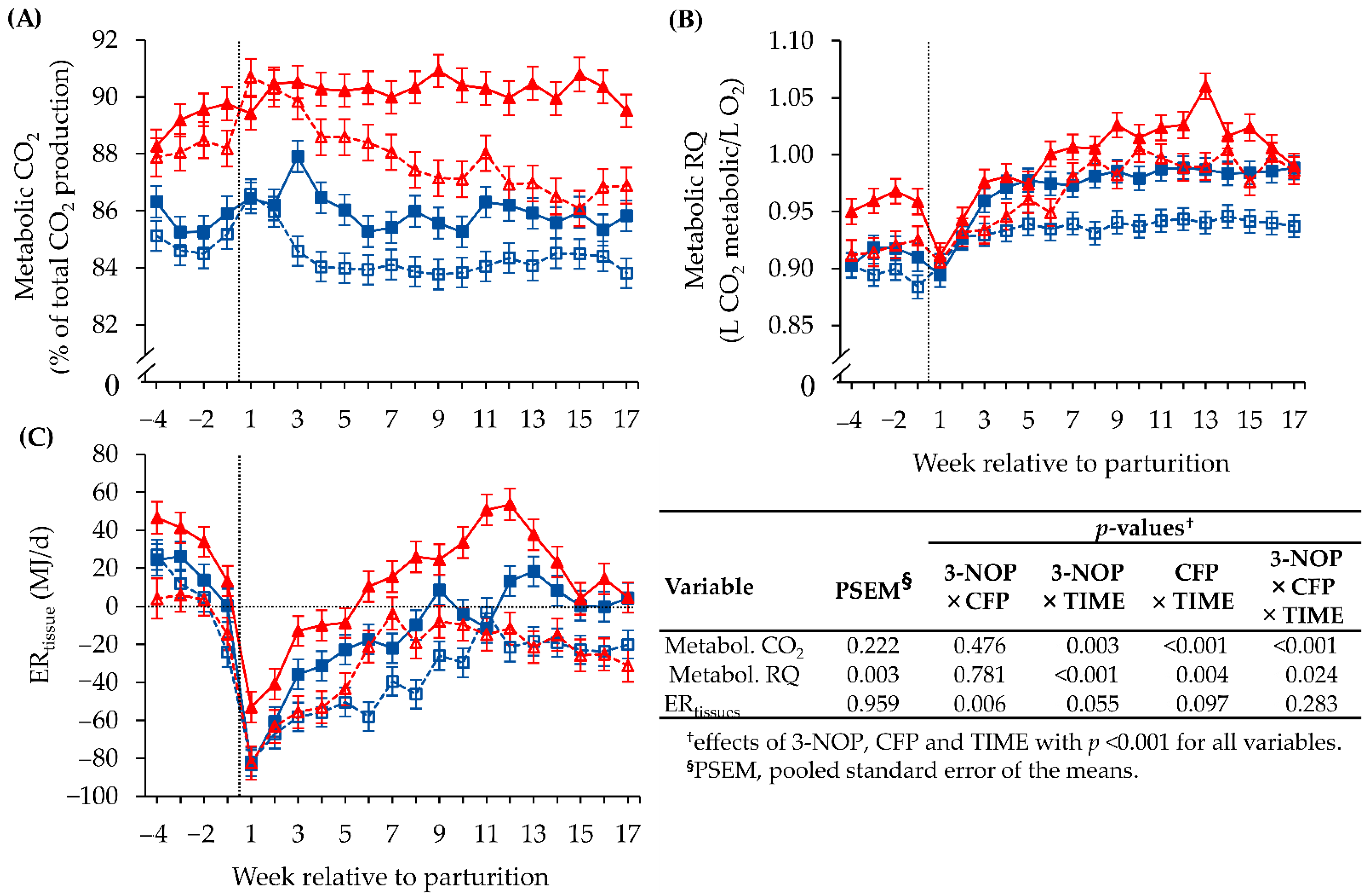
Dairy | Free Full-Text | Assessment of Metabolic Adaptations in Periparturient Dairy Cows Provided 3-Nitrooxypropanol and Varying Concentrate Proportions by Using the GreenFeed System for Indirect Calorimetry, Biochemical Blood Parameters and ...

Effects of 3-nitrooxypropanol (3-NOP), concentrate feed proportion and... | Download Scientific Diagram
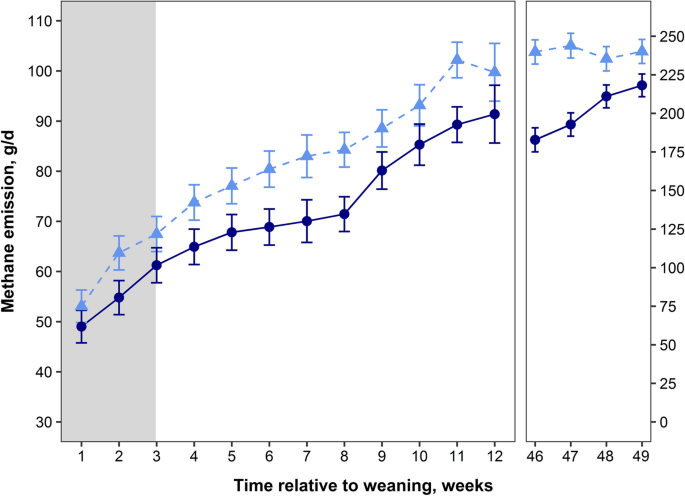
Early life dietary intervention in dairy calves results in a long-term reduction in methane emissions | Scientific Reports

The effect of 3-nitrooxypropanol, a potent methane inhibitor, on ruminal microbial gene expression profiles in dairy cows | Microbiome | Full Text
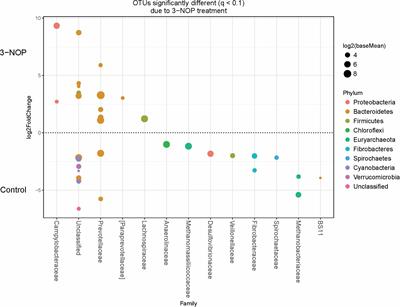
Frontiers | 3-NOP vs. Halogenated Compound: Methane Production, Ruminal Fermentation and Microbial Community Response in Forage Fed Cattle

Binding of 3-NOP to methyl-coenzyme M reductase (MCR) as suggested by... | Download Scientific Diagram

Safety and efficacy of a feed additive consisting of 3‐nitrooxypropanol (Bovaer® 10) for ruminants for milk production and reproduction (DSM Nutritional Products Ltd) - - 2021 - EFSA Journal - Wiley Online Library





